What is Induction Cooking, how it works and how to use it

Induction cooker has become very popular in recent times.
What is an Induction Cooker?
Other cookers use a heat transfer mechanism to heat the cooking vessel or cookware. In traditional cookers, heat is transferred from a heated electric coil or burning gas, oil or firewood or other similar material. All these cookers use a cooking stove or cooktop for placing the cookware.
In an induction cooker, heat is not transferred to the cookware from anywhere else. Instead, heat is generated in the cookware itself using a process called induction heating. In this process, an electrically conducting object or in other words, an object made of a magnetic material like Iron, is heated by electromagnetic induction. Generally you can find an electromagnetic induction in equipment like electric motors, induction motors, transformers, generators etc. A high frequency electric current is passed through the electromagnet and as a result, a high-frequency electromagnetic field is created.
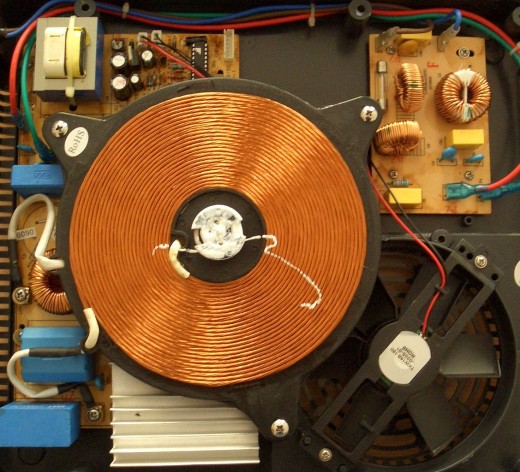
When a pot or some other cookware made of or consisting of magnetic material is placed on an induction cooker, the electromagnetic field transfers energy (not heat) to the bottom of the cookware. This causes the pot and the food inside the pot to become hot. By changing the strength of the electromagnetic field, you can control the amount of heat generated in the cookware and thereby change the temperature of the cookware.

Induction Cookware
The cookware made of or consisting of magnetic material means either the cookware made of Iron or magnetic stainless steel or otherwise any cookware which has a bottom made of Iron or magnetic stainless steel. Therefore, with an induction cooker, you can use cookware such as stainless steel pots, Stainless steel rice cookers, cast iron frying pots, oil boiling pots, stainless steel water jugs, cast iron pots, grilling iron plates etc. However the most important point to note is that the base of the pot should be flat and has a diameter between 12cm to 25cm (depending on the type of the induction cooker). This is the approximate size of the electromagnetic induction available in the inside of the cooker.
Cookware not suitable for induction cooking
Other cookware like pots or vessels made of ceramic, aluminium, copper or heat-resistant glass as well as the pots with a base made of these materials cannot be used with an induction cooker. Also, pots without a flat base and pots with a flat base outside the above size cannot be used on an induction cooker.
Advantages of Induction cookers
Induction cooker is faster than the traditional electric cooker because in induction cooking, the cookware acts as the heat source resulting in much faster and more even heating. Thus it reduces the cooking time by more than one third compared to traditional cookers. It is also much more energy efficient. The induction cooker does not make use of open flame or fire or any heating elements which are heated to the reddish colour. Therefore, the likelihood of burn injury is considerably less than with traditional methods. The induction cooking process does not emit smoke or carbon. When cooking, the cooker and the surrounding area remain cool. This allows you to cook in a cool and comfortable environment. The induction cooker has a compact design and the cooking plate stays cool. This means the cooker is always safe to use. Also, it allows you to cook anywhere in your home even on your dining table.

This is what Walmart say about the GE Induction Cooker :

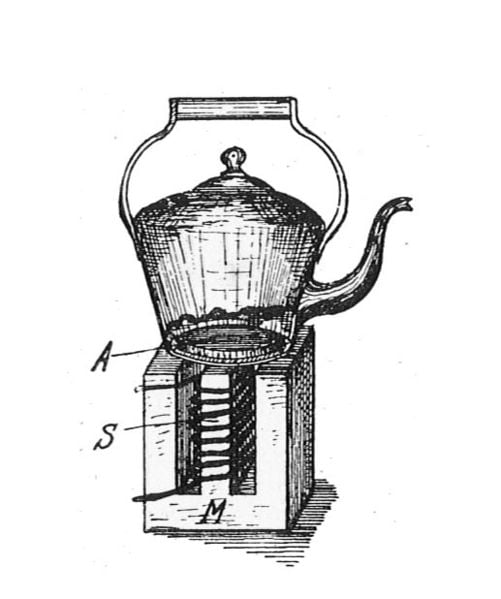
History of the Induction Cooker
Induction Cooker is not a new concept or a new invention. The first induction cooker has been patented in early 1900s. The picture here extracted from Rankin Kennedy, Electrical Installations, Vol II, 1909 edition explains the basics of an early induction cooker. Letter S denotes a coil of copper wire which creates an electromagnetic field in magnetic core denoted by the letter M. This electromagnetic field passes through the bottommost part of the iron kettle (letter A) and induces eddy currents within the iron kettle causing the pot to generate heat in it. However, in modern induction cookers, electronically generated high frequency electric current is used to create the electromagnetic field. This can be seen in the picture (above) of the inside view of a modern induction cooker.
Parts of a modern portable Induction Cooker
The diagram below illustrates the main parts of a modern portable Induction Cooker.
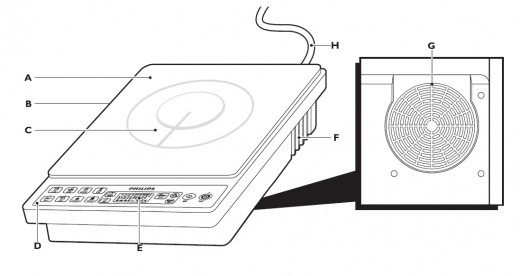
A Microcrystal cooking plate
B Body
C Cooking zone
D Control panel
E Display
F Air outlet
G Air inlet
H Mains cord
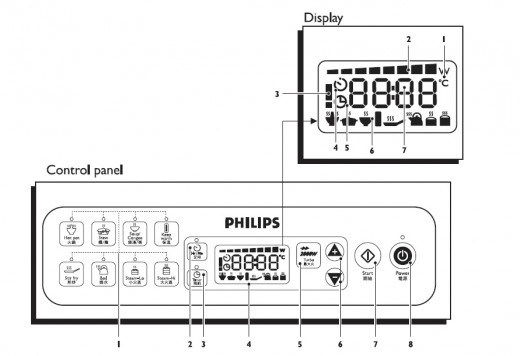
Control panel
1 Preset cooking modes with indicator lights
2 Hr:Min button (cooking time)
3 Timer button
4 Display
5 Turbo button
6 +/- buttons (for setting cooking time, power level and cooking
temperature)
7 Start button
8 Power on/off button
Display
1 Power (W)/temperature (°C) symbol
2 Power level
3 Error symbol
4 Cooking time
5 Timer indicator
6 Preset cooking mode symbols
7 Cooking time/power level/cooking temperature indication




Design of Modern Induction Cookers
The cooking surface of an induction cooker is made of a glass-ceramic, a polycrystalline material which is produced through crystallization of normal glass. Glass-ceramic is a strong material and it can sustain quick temperature changes. It is also a poor heat conductor. Therefore, glass-ceramic is used to make cooktops or cooking plates. With the use of glass-ceramic only a little heat is passed through the bottom of the pot to the cooking plate. In normal circumstances, the cooking plate remains cool enough to touch without burn injury after the cooking is over. However, manufacturers always warn the users not to touch the cooking plate immediately after cooking pot is removed from the cooker. Even though glass-ceramic is a strong material, it is not totally unbreakable. Therefore, manufacturers limit the weight of the cookware (along with food inside) placed on the cooking plate because if the weight exceeds the specified limit the cooking plate could be broken.
Induction cookers may have 1 to 4 induction zones, but even five zones are possible. Two coils are most common in many countries. Portable induction cookers with a single induction zone have become much popular in many countries specially in Asia.
© 2012 Lasantha Wijesekera



